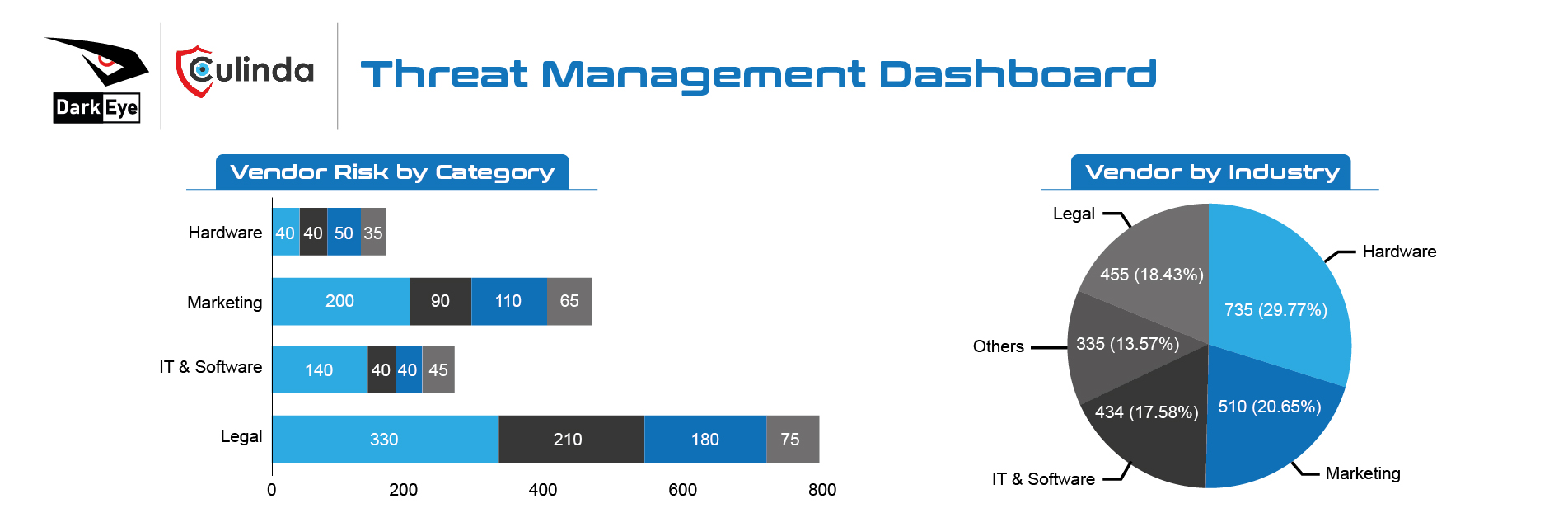
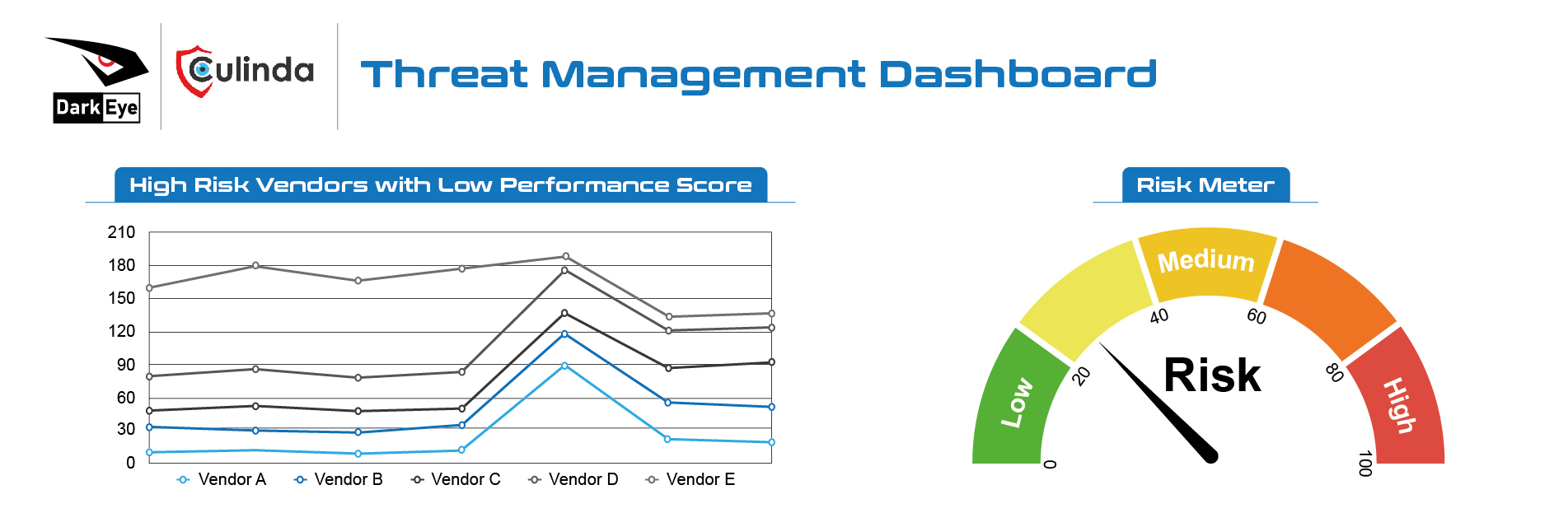
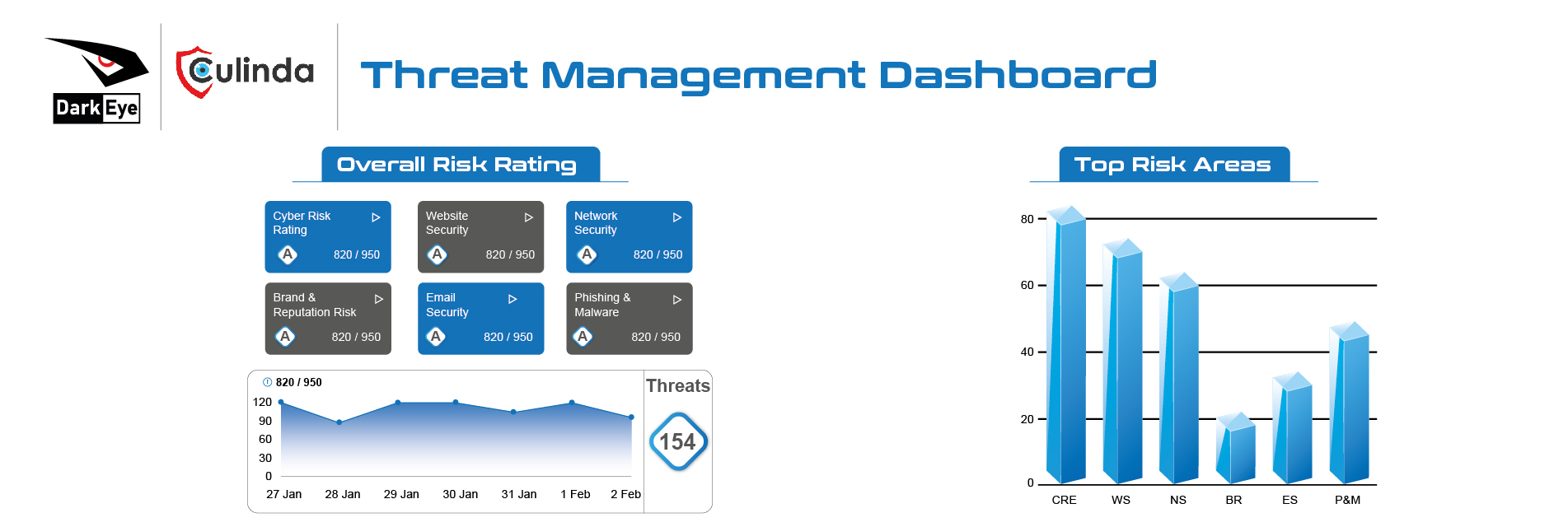
OSINT Strategy
- Cyber security tools
- Intelligence domains which include the search, selection, and collection of intelligence information, from publicly available sources
- Performed through monitoring, analysis, and research of information coming from the Internet
- OSINT is information that has been deliberately discovered, discriminated, distilled, and disseminated for a select audience
- Materials compiled based on information from open sources support all intelligence methods and activities through accumulation of intelligence knowledge, its analysis and dissemination
- OSINT + HI = VA OSINT (OSINT Validated)


Our Value Proposition
- OpenSource Intelligence Collection – Reported from cybercriminals, social media engagement, marketplaces, and chat rooms with the touch of Human Intelligence Collection
- Real-time Threat Tracking – Indicators of compromise, threat actors, malware
- Vulnerability and Credential Intelligence – Vulnerability scoring, compromised credentials of customers, partners, vendors, VIPs, executives
- Reduction of Risk – Security posture of organization mapped against discovered organization assets across surface, deep and dark web
Deep and Dark Web
- Surface Web
- Deep Web
- Dark Web
- The value of information cannot be realized unless it is possible to find it
- Most common methods are paste sites and forums
- Cached content is very important

Marketplace

Healthcare

Legal

Insurance
Manufacturing

Background Checks

Banks

Cyber Insurance

Sports

Venues Entertainment

Executive Protection
Threat Intelligence Use Cases

Brand Management and Protection

Self-Assessment

Merger & Acquisition Due Diligence

Compromised Credentials

Insider Threat

Cyber Insurance

Vendor Risk Management
Threat Intelligence
Vulnerability Management

Threat Hunting

Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
- Focuses on analyzing raw data gathered from recent and past events to monitor, detect, and prevent threats to an organization
- Details of the motivations, intent, and capabilities of internal and external threat actors (e.g., Government, Organized crime, Activists, State-sponsored criminals)
- Threat intelligence includes specifics on the tactics, techniques, and procedures of these adversaries
- Threat intelligence’s primary purpose is to inform business decisions regarding the risks and implications associated with threats
- Shifting the focus from reactive to preventive intelligent security measures
CTI Monitoring
- Network Threats – Ability to monitor the risk of exposure of an entire country and/or specific organization (e.g., Infected systems, malware and botnets)
- Monitoring and take down of phishing sites
- Identification of compromised bank accounts Internationally – Reporting leaked credit card transactions to money mules
- Monitoring underground cybercrime forums and the Deep/Dark Web to discover compromised bank accounts.
- Rogue Mobile Application – Unauthorized mobile application developed to look like and behave like a legitimate one
- Monitoring Threats from Third Parties – Continuous auditing, security controls and monitoring controls

Benefits of CTI
- Prevent data loss
- Detect breaches
- Threat analysis
- Data analysis
- Incident response
- 24/7 threat intelligence, monitoring and analysis
- Rapid identification and remediation of attacks
- Ability to assess risk and prioritize threats
Leveraging the CTI Process (Intelligence Cycle)
Processing & Production
- Identifying the organization’s requirements to create the right amount of intelligence out of information
Planning & Evaluation
- Ensuring processes and tools are in place. Conducting risk assessments to identify threats, take steps to close potential gaps and implement controls
Collection
- Acquiring raw data to process.
Dissemination
- Supplying the relevant teams with finished and processed intelligence products to address the threats


Threat Intelligence with Return on Investment
Industry Leading Intelligence
Automated, human intelligence collection and finished intelligence reporting from cybercriminal forums, marketplaces, chat rooms and online engagements
Reduction of Risk
An industry leading intelligence requirements program that enables organizations to map intelligence collection and outputs to business drivers and risk reduction
Real-time Malware Tracking
Automated and technical tracking of malware including IoCs, TTPs, YARA, IDS signatures and technical intelligence reports
Vulnerability and Credential Intelligence
Vulnerability intelligence to drive your patching priorities and compromised credentials of your employees, VIPs and customers
IoCs
Tactical Intelligence (Short-term)
Information from known attacks, which has the potential to immediately influence cybersecurity decision-making
Operational Intelligence (Mid-term)
Offers insight into threat actors’ motivations, capabilities and objectives, and helps teams assess specific incidents relating to events and investigations, and guides and supports incident response
Strategic Intelligence (Long-term)
Broader and higher-level abstracts of the data to identify threats associated with foreign policy, global events etc., and focuses on the long-term impacts of cyber threats
Technical Threat Intelligence (TTI)
TTI is information that is normally consumed through technical resources. TTI typically feeds the investigative or monitoring functions of an organization, for example firewalls and mail filtering devices, by blocking attempted connections to suspect servers. TTI also serves for analytic tools, or just for visualization and dashboards

Threat Intelligence Sources
| Internal Sources | External Sources | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example | Technologies for collecting and processing | Vulnerabilities databases, IP blacklists and whitelists, threat data feeds | Forums, news sites, social media, dark web | |
| Technologies for collecting and processing | Feed parser | Feed/web scraper, parser | Collection: crawlers, feed/web parsers Processing: Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning | |